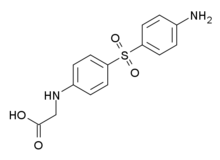
Acediasulfone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 80-03-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 66451 |
| ChemSpider |
59823 |
| UNII |
30YP2YHH8W |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL48396 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H14N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 306.337 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Acediasulfone (INN) is an antimicrobial drug, which also has antimalarial activity. It is a long-acting prodrug of dapsone, which is used for treating leprosy.
Synthesis
Dapsone is somewhat inconvient to administer to patients because of its rather low water solubility.
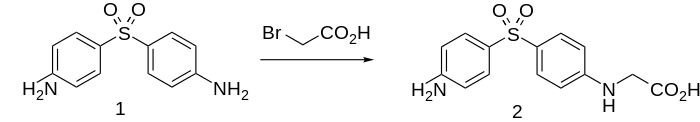
Acediasulfone synthesis:[1] CH 254803 and CH 278482 (1949, 1952, to Cilag Ltd.); Rawlins, U.S. Patent 2,589,211 (1952 to Parke Davis).
In the search for more easily administered drugs, 1 was reacted with bromoacetic acid to give acediasulfone (3) which can be adminsistered as a water soluble salt.
References
- ↑ Jackson, Ernest L. (1948). "Certain N-Alkyl, N-Carboxyalkyl and N-Hydroxyalkyl Derivatives of 4,4'-Diamino-diphenyl Sulfone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 70 (2): 680–4. doi:10.1021/ja01182a074. PMID 18907772.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.